Introduction
Accounting professionals tend to work under pressure so that they can cover as much ground as possible. However, tools at their disposal often have very limited power and are unable to optimistically fit their workflow. Furthermore, their work is prone to errors due to too many copy+paste and unreproduciblity.
In my view, R is a perfect tool to increases their productivity and conform to their workflow. Watch Hadley Wickham on Data Science Challenges and Data visualization and data science, Hadley Wickham to learn more about it.
Data analytics lifecycle described by R4DS sensibly matchs audit routines. This document is meant to demonstrate the usefulness of R in the field of audit via a specific use case. Visit my github repo for project details.
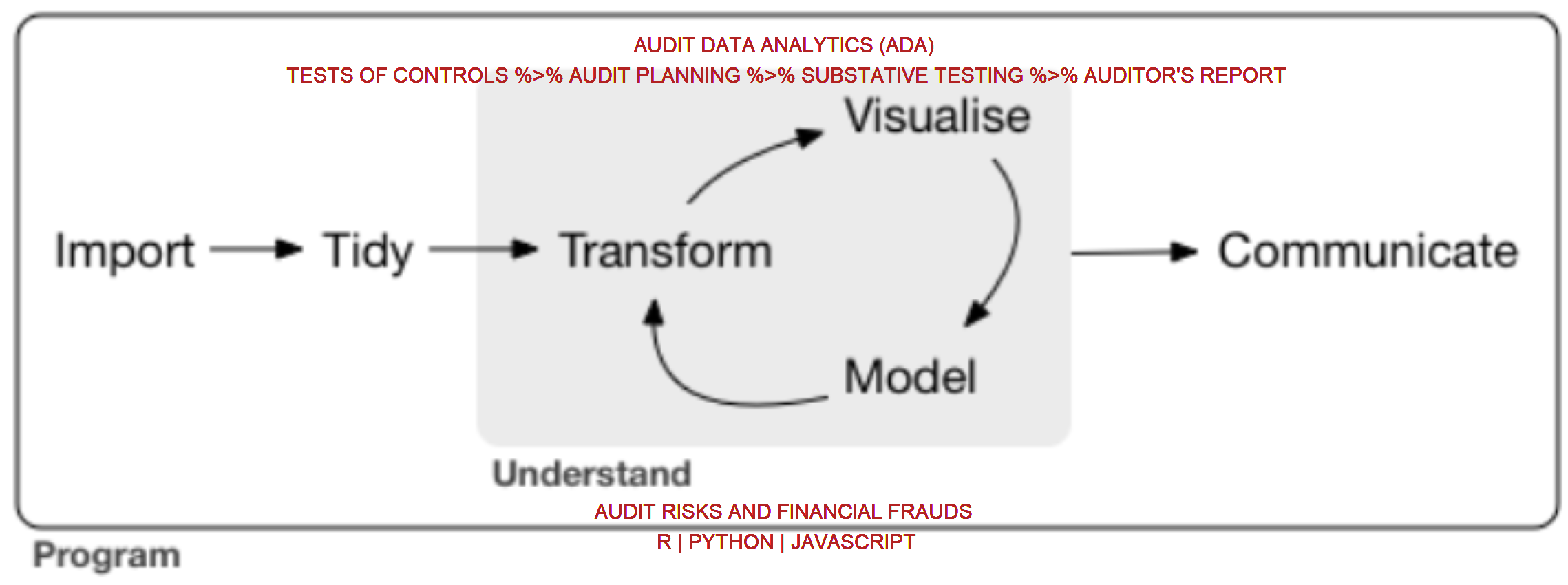
Data preparation
Data scientists spend 80% of their time getting the data into desired shape and only 20% of their time on actual data analysis.
The case study assumes that auditors are at the stage of audit planning and will use R to perform audit procedures. To obtain data, auditors will typically go through media coverage, company announcements and Genernal Ledger (Database or PBC). R has excellent tools for webscrapping, pdf table extraction and SQL queries.
Unless there are unknown bank accounts, all company transactions will be recorded in G/L. G/L contains valuable information for auditors to perform risk assessment and preliminary analytical procedures efficiently and effectively. Unfortunately, auditors often have difficulties in cleaning G/L and extracting information out of G/L. This is particularly true in the case of JV memo or description. Using R to solve those issues would be like a breeze.
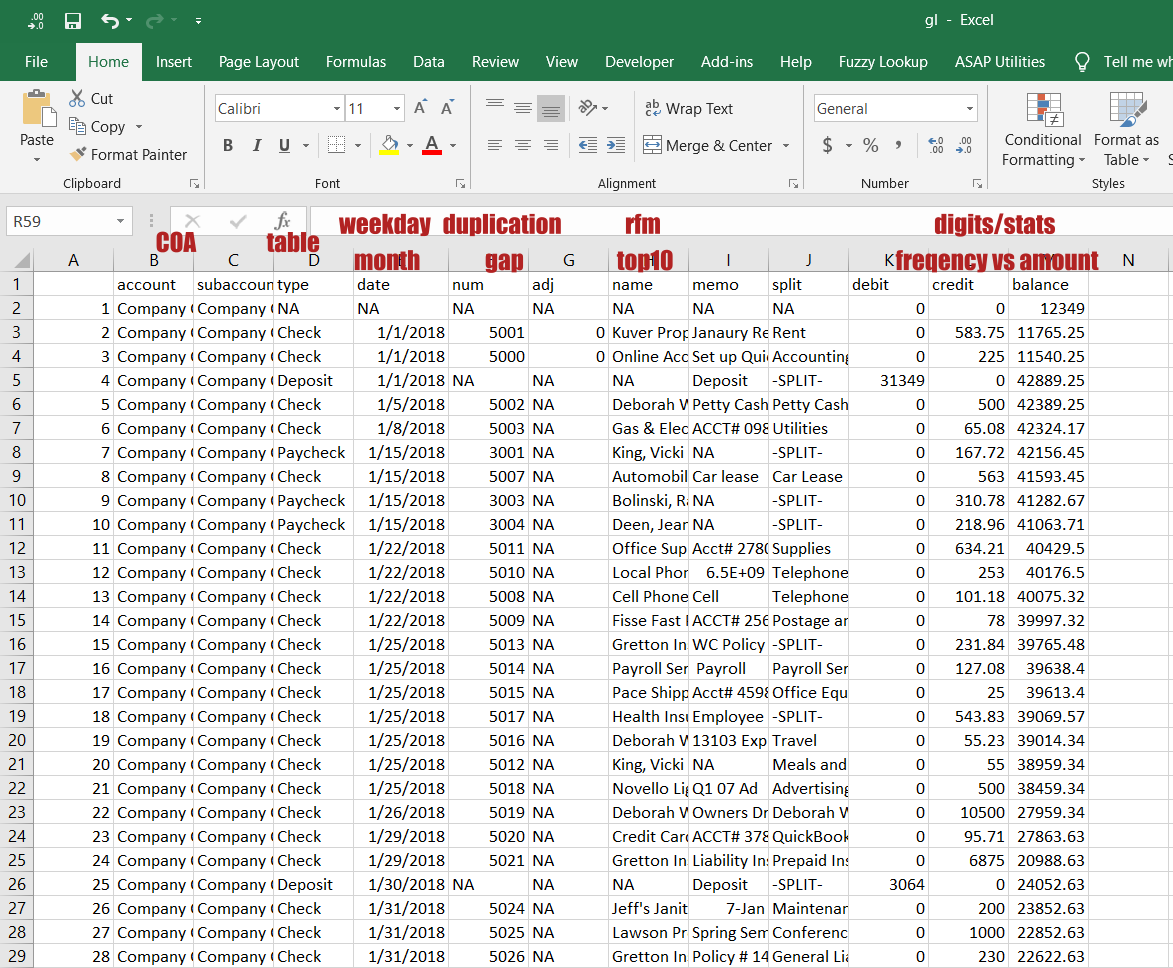
Dataset
# A tibble: 10 x 14
id account subaccount type date num name memo split debit
<dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 2 Compan~ Company C~ Check 2018-01-01 5001 Kuve~ Jana~ Rent 0
2 3 Compan~ Company C~ Check 2018-01-01 5000 Onli~ Set ~ Acco~ 0
3 4 Compan~ Company C~ Depo~ 2018-01-01 <NA> <NA> Depo~ -SPL~ 31349
4 5 Compan~ Company C~ Check 2018-01-05 5002 Debo~ Pett~ Pett~ 0
5 6 Compan~ Company C~ Check 2018-01-08 5003 Gas ~ ACCT~ Util~ 0
6 7 Compan~ Company C~ Payc~ 2018-01-15 3001 King~ <NA> -SPL~ 0
7 8 Compan~ Company C~ Check 2018-01-15 5007 Auto~ Car ~ Car ~ 0
8 9 Compan~ Company C~ Payc~ 2018-01-15 3003 Boli~ <NA> -SPL~ 0
9 10 Compan~ Company C~ Payc~ 2018-01-15 3004 Deen~ <NA> -SPL~ 0
10 11 Compan~ Company C~ Check 2018-01-22 5011 Offi~ Acct~ Supp~ 0
# ... with 4 more variables: credit <dbl>, balance <dbl>, weekday <ord>,
# month <ord>Data dictionary
Completeness test
Chart of Accounts (COA)
Control total
“b/f + current year = c/f” cannot be performed due to the lack of prior year.
# A tibble: 1 x 2
debit credit
<dbl> <dbl>
1 2136029. 2136029.Range of date
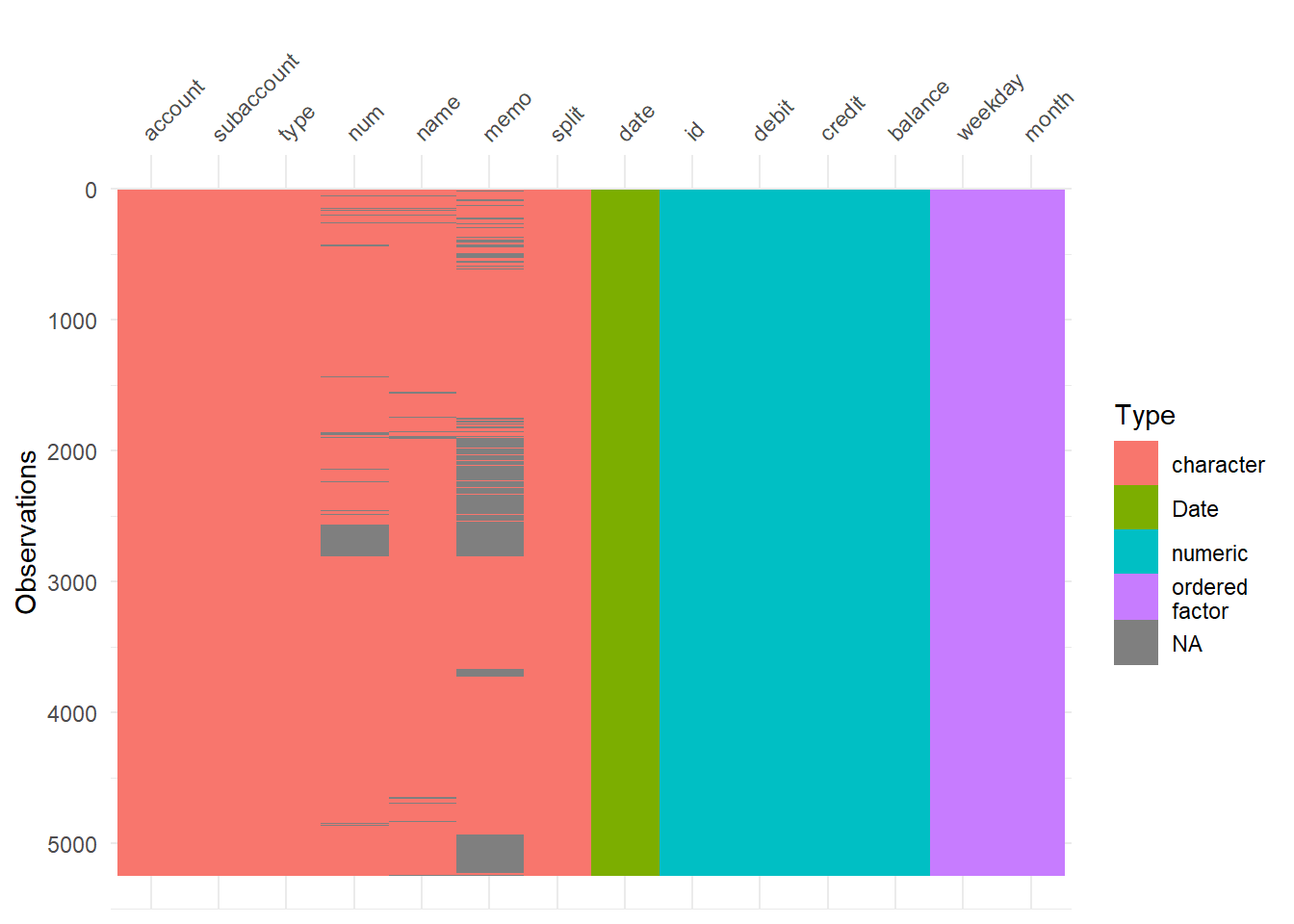
[1] "2018-01-01" "2018-12-31"Missing values
Round numbers
# A tibble: 36 x 8
id account subaccount type date num debit credit
<dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <date> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 27 Company Che~ Company Checki~ Check 2018-01-31 5025 0 1000
2 40 Company Che~ Company Checki~ Transf~ 2018-02-09 <NA> 0 10000
3 101 Company Che~ Company Checki~ Check 2018-03-26 5075 0 10000
4 172 Company Che~ Company Checki~ Check 2018-05-25 5124 0 12000
5 210 Company Che~ Company Checki~ Bill P~ 2018-06-29 5156 0 1000
6 226 Company Che~ Company Checki~ Transf~ 2018-07-20 <NA> 0 10000
7 240 Company Che~ Company Checki~ Check 2018-07-25 5179 0 10000
8 272 Company Che~ Company Checki~ Check 2018-08-22 5206 0 3000
9 279 Company Che~ Company Checki~ Check 2018-08-27 5214 0 12000
10 320 Company Che~ Company Checki~ Bill P~ 2018-10-05 3079 0 6000
# ... with 26 more rows999 numbers
# A tibble: 11 x 8
id account subaccount type date num debit credit
<dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <date> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 403 Company Chec~ Company Checkin~ Payc~ 2018-12-15 5365 0 340.
2 883 Inventory As~ Inventory Asset Invo~ 2018-04-16 71087 0 49.0
3 971 Inventory As~ Inventory Asset Invo~ 2018-05-16 71095 0 98.0
4 1029 Inventory As~ Inventory Asset Invo~ 2018-05-24 71086 0 49.0
5 1082 Inventory As~ Inventory Asset Invo~ 2018-06-07 71085 0 49.0
6 1495 Inventory As~ Inventory Asset Invo~ 2018-12-10 71105 0 98.0
7 4027 Purchases (~ Purchases (Cos~ Invo~ 2018-04-16 71087 49.0 0
8 4112 Purchases (~ Purchases (Cos~ Invo~ 2018-05-16 71095 98.0 0
9 4170 Purchases (~ Purchases (Cos~ Invo~ 2018-05-24 71086 49.0 0
10 4220 Purchases (~ Purchases (Cos~ Invo~ 2018-06-07 71085 49.0 0
11 4615 Purchases (~ Purchases (Cos~ Invo~ 2018-12-10 71105 98.0 0JV posted on weekends
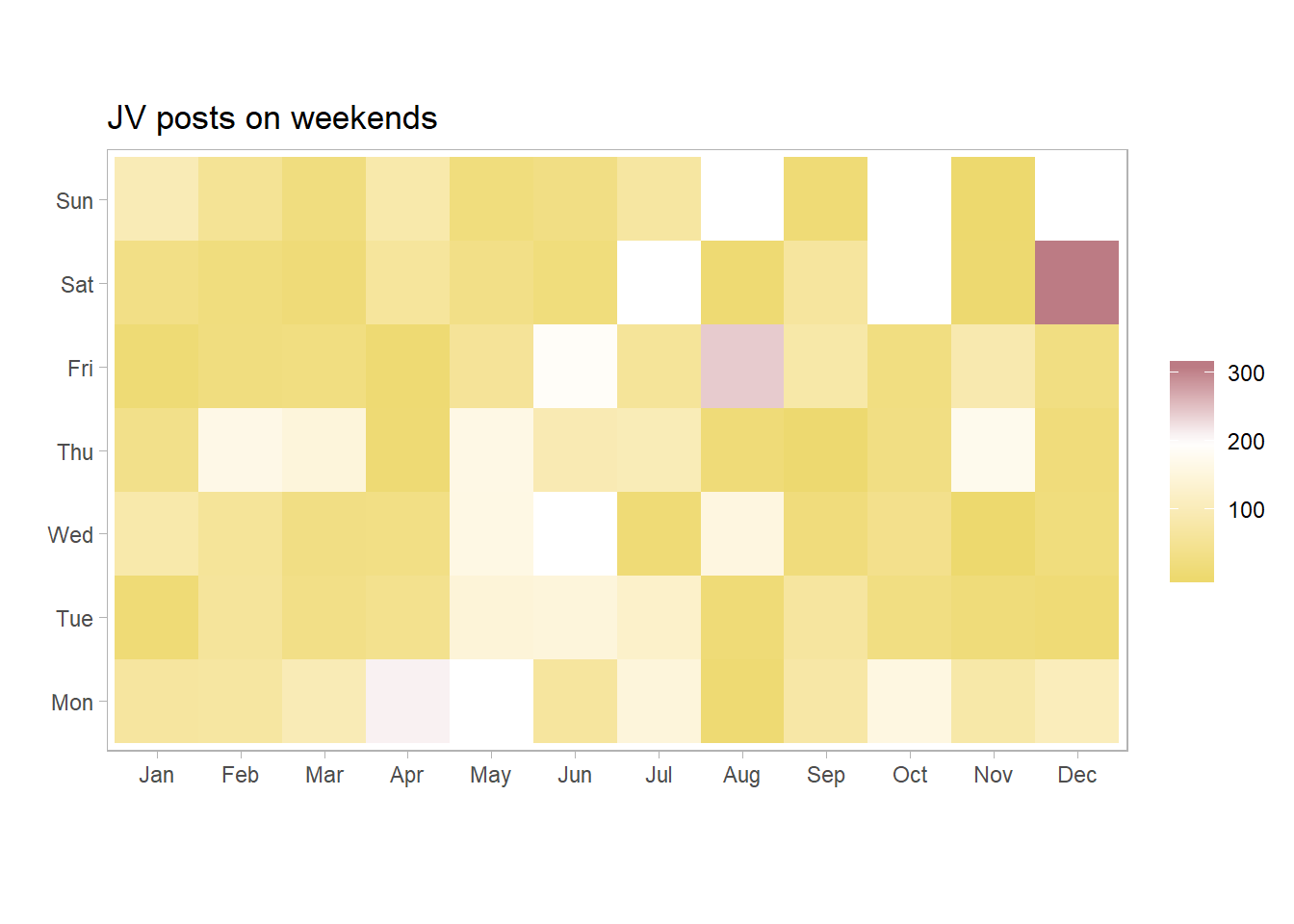
Top 10 JVs posted on weekends are;
# A tibble: 10 x 3
type account n
<chr> <chr> <int>
1 Invoice Revenue 165
2 Invoice Inventory Asset 164
3 Invoice Purchases (Cost of Goods) 164
4 Paycheck Payroll Liabilities 153
5 Paycheck Wages 76
6 Deposit Undeposited Funds 52
7 Liability Check Payroll Liabilities 44
8 Paycheck Company Checking Account 19
9 Invoice Accounts Receivable 18
10 Paycheck Direct Labor 17Monthly accumulated FS
# A tibble: 6 x 7
subaccount Jan Feb Mar Oct Nov Dec
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Accounting Fees 225 0 0 2544 0 0
2 Accounts Payable -35903 -45421 -21732. -4438. -6517. -16697.
3 Accounts Receivable 22443. 10455. 16399. 35194. 16227. 32333.
4 Accumulated Depreciation -76.9 -154. -231. -769. -846. -923.
5 Advertising Expense 500 0 0 2000 0 0
6 Business License & Fees 0 710. 0 0 0 0